Dr. Shawn Allen has either authored or reviewed and approved this content.
Page Updated:If you’re struggling with nasal congestion, frequent sinus infections, snoring, or sleep apnea, a deviated septum may be to blame. Dr. Shawn Allen, Board-Certified Otolaryngologist (ENT) and fellowship-trained Rhinologist, specializes in advanced sinus care, including minimally invasive septoplasty procedures designed to restore normal breathing.
With outpatient septoplasty, Dr. Allen helps patients from Houston, The Woodlands, and nearby communities experience lasting relief and improved quality of life.

The nasal septum is a thin wall of bone and cartilage that separates the nasal cavity into two nasal passages. The septum is intended to divide the left and right nasal passages equally, but up to 80% of people have a crooked septum, also known as a deviated septum.
This condition may:
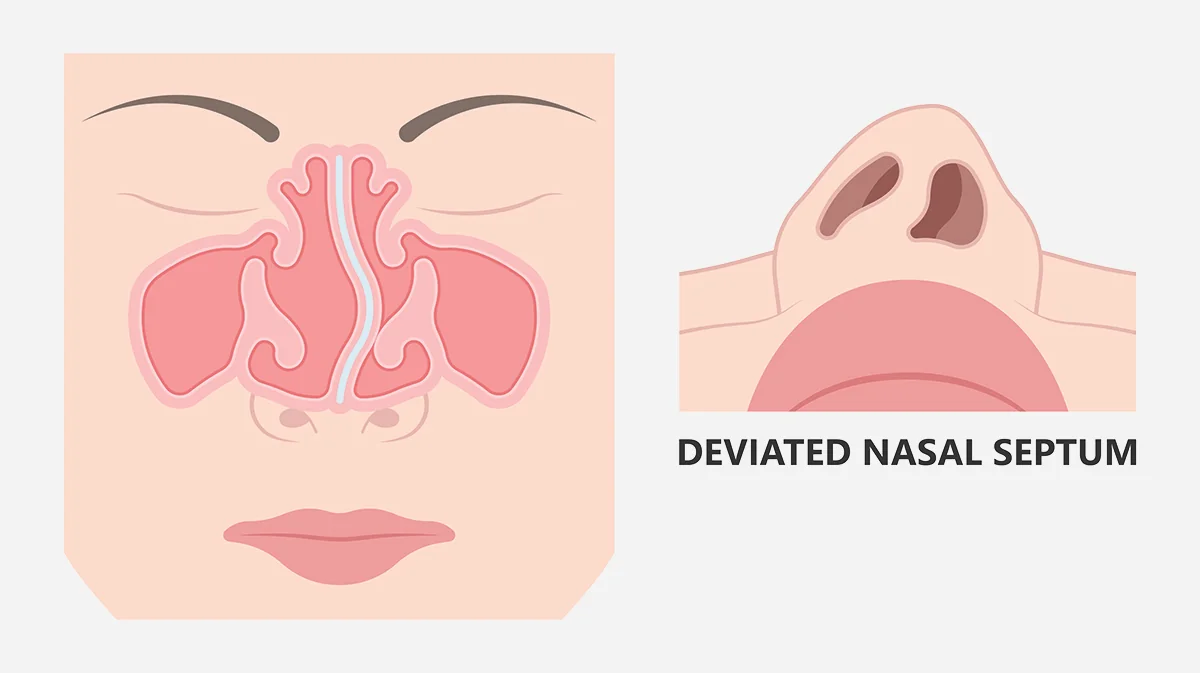

Depending on the severity of the deviation, a deviated septum can restrict airflow and may cause a number of symptoms. Snoring is the most noticeable symptom for many patients with a deviated septum. Additional symptoms include:
Swollen turbinates, small bony plates surrounded by mucosal lining found within the nasal passages, may cause some of the symptoms associated with a deviated septum. Septoplasty and turbinate reduction may be performed for some patients to alleviate nasal obstruction.
It is generally not necessary to fix a deviated septum in cases where it causes mild to no symptoms. However, an otolaryngologist may recommend a septoplasty procedure for patients whose deviated septum causes breathing problems, chronic sinus infections, sleep apnea, or other problems.

Septoplasty is a same-day, outpatient procedure performed under local or general anesthesia. Dr. Allen uses advanced endoscopic techniques to:
Depending on the case, the procedure may involve:
Dr. Allen uses a precision-focused, comfort-first approach to maximize results and minimize downtime.
Through a small incision, Dr. Allen will lift the mucous membrane that covers the septum (the mucosa) to access the bone and cartilage below. He will then reshape the septum, sometimes removing parts of bone and/or cartilage. Dr. Allen may also use cartilage splints (spreader grafts) to support the septum. He will ensure that the septal support mechanism is as straight as possible and continues to provide needed structural support for the nasal tip before repositioning the mucosa and closing the incision on the septum with dissolvable sutures.
Once the septoplasty surgery is complete, Dr. Allen may insert splints within the nasal cavities to hold the septum in place as it heals, but most cases do not require these splints. Nasal packing is no longer used routinely, and any packing material used is biodegradable and no longer obstructs nasal breathing during the healing process.
Before your procedure, you’ll meet with Dr. Allen for a full evaluation. This includes:
If you’re a candidate for surgery, Dr. Allen will explain the procedure in detail and provide clear pre- and post-operative instructions to guide your recovery.
Most patients can go home the same day for recovery from the septoplasty procedure. In the first few days, it’s normal to experience some swelling, discomfort, nasal drainage, or mild bleeding. While the bleeding usually stops within a few hours, Dr. Allen recommends taking precautions for about 10 days to avoid irritating the healing area. This includes:
Swelling and nasal congestion typically peak around day 2 or 3 after surgery, then gradually improve over the next week to 10 days. Discomfort is usually mild to moderate and may be felt in the nose, the roof of the mouth, or even the front teeth.
To support healing, Dr. Allen will encourage you to:
Most patients can return to work within a week. You’ll likely need to wait 10 to 14 days before resuming exercise or more intense physical activity.
What are the risks of septoplasty?
As with any surgery, risks include bleeding, infection, or changes in nasal shape. However, complications are rare when performed by an experienced ENT like Dr. Allen.
How long is recovery?
Most patients feel significantly better within 7–10 days, with full healing over several weeks.
How much does septoplasty cost?
Costs may vary depending on insurance and any combined procedures. Dr. Allen’s team will help you navigate coverage and provide a detailed cost estimate.
If a deviated septum is causing you to experience nasal obstruction, snoring, frequent sinus infections, or other symptoms, consulting with a Board-Certified Otolaryngologist (ENT) who specializes in treating nasal and sinus conditions is the best way to achieve lasting relief. If you live in Houston, The Woodlands, or surrounding areas in Texas, ear, nose, and throat specialist Dr. Shawn Allen can perform an outpatient septoplasty procedure to help you breathe more easily and feel better. To schedule a consultation with Dr. Allen, please contact us today.
1 American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. Deviated Septum. Available: https://www.enthealth.org/conditions/deviated-septum/. Accessed December 19 2022.
2 Cleveland Clinic. Deviated Septum. Available: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16924-deviated-septum. Accessed December 19, 2022.
3 Mayo Clinic. Septoplasty. Available: https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/septoplasty/about/pac-20384670. Accessed December 19, 2022.
4 Cleveland Clinic. Septoplasty. Available: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17779-septoplasty. Accessed December 19, 2022.
5 American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery. Deviated Septum. Available: https://www.enthealth.org/conditions/deviated-septum/. Accessed December 19 2022.
Dr. Shawn Allen has either authored or reviewed and approved this content.
Page Updated: